侏儒排序
侏儒排序(英语:Gnome Sort)或愚人排序(英语:Stupid Sort)是一种排序算法,最初在2000年由伊朗计算机工程师Hamid Sarbazi-Azad(谢里夫理工大学计算机工程教授)提出,他称之为“愚人排序”[1]。此后Dick Grune也描述了这一算法,称其为“侏儒排序”[2]。此算法类似于插入排序,但是移动元素到它该去的位置是通过一系列类似冒泡排序的移动实现的。从概念上讲侏儒排序非常简单,甚至不需要嵌套循环。它的平均运行时间是O(n2),如果列表已经排序好则只需O(n)的运行时间。[3]
| 侏儒排序 | |
|---|---|
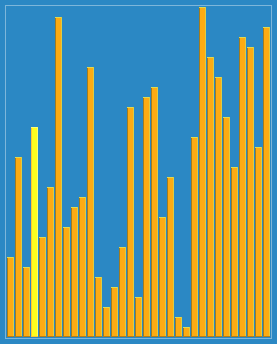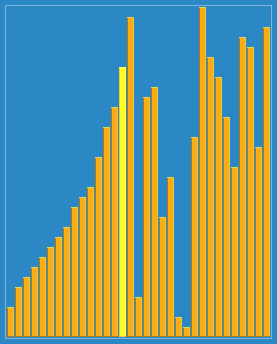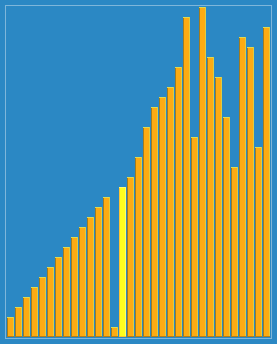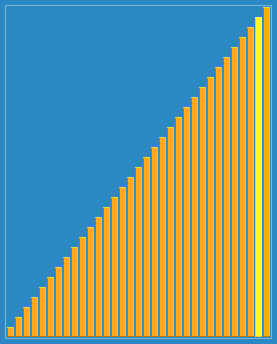 使用侏儒排序法对一列数字进行排序的过程 | |
| 概况 | |
| 类别 | 排序算法 |
| 数据结构 | 数组 |
| 复杂度 | |
| 平均时间复杂度 | |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | |
| 最优时间复杂度 | |
| 空间复杂度 | 辅助空间 |
| 最佳解 | No |
| 相关变量的定义 | |
解释
procedure gnomeSort(a[]):
pos := 0
while pos < length(a):
if (pos == 0 or a[pos] >= a[pos-1]):
pos := pos + 1
else:
swap a[pos] and a[pos-1]
pos := pos - 1
样例
给定一个未排序的数组a = [5, 3, 2, 4],侏儒排序在while循环中执行以下步骤。粗体表示pos变量当前所指的元素。
| 当前数组 | 下一步操作 |
|---|---|
| [5, 3, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1],交换 |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1],pos自增 |
| [3, 5, 2, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1],交换;pos > 1,pos自减 |
| [3, 2, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1],交换;pos <= 1,pos自增 |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1],pos自增 |
| [2, 3, 5, 4] | a[pos] < a[pos-1],交换;pos > 1,pos自减 |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1],pos自增 |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | a[pos] >= a[pos-1],pos自增 |
| [2, 3, 4, 5] | pos == length(a),完成 |
实现示例
Julia (编程语言)
# Julia Sample : GnomeSort
function GnomeSort(A)
pos = 1
while pos<length(A)+1
if (pos==1) || (A[pos]>=A[pos-1])
pos+=1
else
A[pos],A[pos-1] = A[pos-1],A[pos]
pos-=1
end
end
return A
end
# Main Code
A = [16,586,1,31,354,43,3]
println(A) # Original Array
println(GnomeSort(A)) # Gnome Sort Array
参考文献
- ^ Sarbazi-Azad, Hamid. Stupid Sort: A new sorting algorithm (PDF). Newsletter (Computing Science Department, Univ. of Glasgow). 2 October 2000, (599): 4 [25 November 2014]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2012-03-07).
- ^ Gnome Sort - The Simplest Sort Algorithm. Dickgrune.com. 2000-10-02 [2017-07-20]. (原始内容存档于2017-08-31).
- ^ Paul E. Black. gnome sort. Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures. U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology. [2011-08-20]. (原始内容存档于2011-08-11).


